一、论文解读
[1] This paper addresses the problem of recognizing free form 3D objects in point clouds.
[2] Compared to traditional approaches based on point descriptors, which depend on local information around points, we propose a novel method that creates a global model description based on oriented point pair features and matches that model locally using a fast voting scheme.
[3] The global model description consists of all model point pair features and represents a mapping from the point pair feature space to the model, where similar features on the model are grouped together.
[4] Such representation allows using much sparser object and scene point clouds, resulting in very fast performance.
[5] Recognition is done locally using an efficient voting scheme on a reduced two-dimensional search space.
[6] We demonstrate the efficiency of our approach and show its high recognition performance in the case of noise, clutter and partial occlusion.
[7] Compared to state of the art approaches we achieve better recognition rates, and demonstrate that with a slight or even no sacrifice of the recognition performance our method is much faster then the current state of the art approaches.
1. Model Globally
scene 和 model ,scene 是我们测得的真实场景(点云),model 是物体的真实模型(点云)。Both the scene and the model are represented as a finite set of oriented points, where a normal is associated with each point.
 points in the scene
points in the scene points in the model
points in the model
 和
和  ,法向量(normals)分别为
,法向量(normals)分别为  和
和  ,
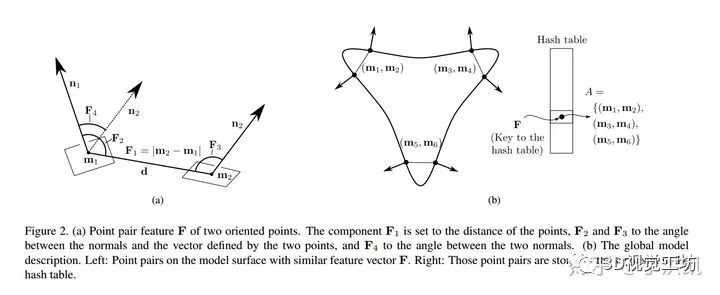
,  ,则 PPF 定义为:
,则 PPF 定义为:
 为两个矢量的夹角,且
为两个矢量的夹角,且  是非对称的。PPF 示意图见 Figure2.(a)。
是非对称的。PPF 示意图见 Figure2.(a)。The model is represented by a set of point pair features with similar feature vectors being grouped together.
 ,其中 distances 和 angles 分别以
,其中 distances 和 angles 分别以  和
和  的步长做采样;
的步长做采样; 的 point pair 放在一起,即哈希表的键(key )为 feature vector
的 point pair 放在一起,即哈希表的键(key )为 feature vector  ,值(value)为具有相同特征矢量的点对集
,值(value)为具有相同特征矢量的点对集  ,如 Figure2.(b) 所示。
,如 Figure2.(b) 所示。The global model description is a mapping from the sampled point pair feature space to the model.
2. Match Locally
 that are similar to a given scene feature
that are similar to a given scene feature  can then be searched in constant time by using
can then be searched in constant time by using  as a key to access the hash table.
as a key to access the hash table. ,假设它在物体的表面上,若假设正确,则在 model 存在一个点
,假设它在物体的表面上,若假设正确,则在 model 存在一个点  与
与  对应;
对应; 的法向轴转动一定角度与 scene 配准
的法向轴转动一定角度与 scene 配准 来描述,将这个 pair
来描述,将这个 pair  定义为 model 相对于参考点
定义为 model 相对于参考点  的Local Coordinates 。
的Local Coordinates 。 ,选取与 scene 点对
,选取与 scene 点对  具有相似 fecture vector
具有相似 fecture vector  (same distance and relative orientation)的 model 点对
(same distance and relative orientation)的 model 点对  ;
; 将
将  移动到 Local Coordinates 的原点,并且转动 model,使其法向轴
移动到 Local Coordinates 的原点,并且转动 model,使其法向轴  与 Local Coordinates 的
与 Local Coordinates 的  轴重合;
轴重合; 对 scene 做相同操作;
对 scene 做相同操作; 绕
绕  轴转动
轴转动  与
与  配准
配准 ,如 Figure 3 所示。
,如 Figure 3 所示。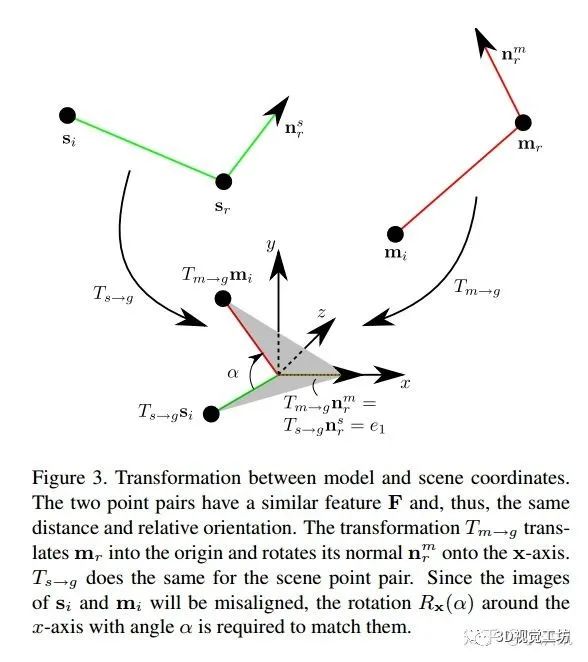
 为 model 采样点
为 model 采样点  的个数,列(columns)数
的个数,列(columns)数  为按采样步长
为按采样步长  的旋转角
的旋转角  的个数。
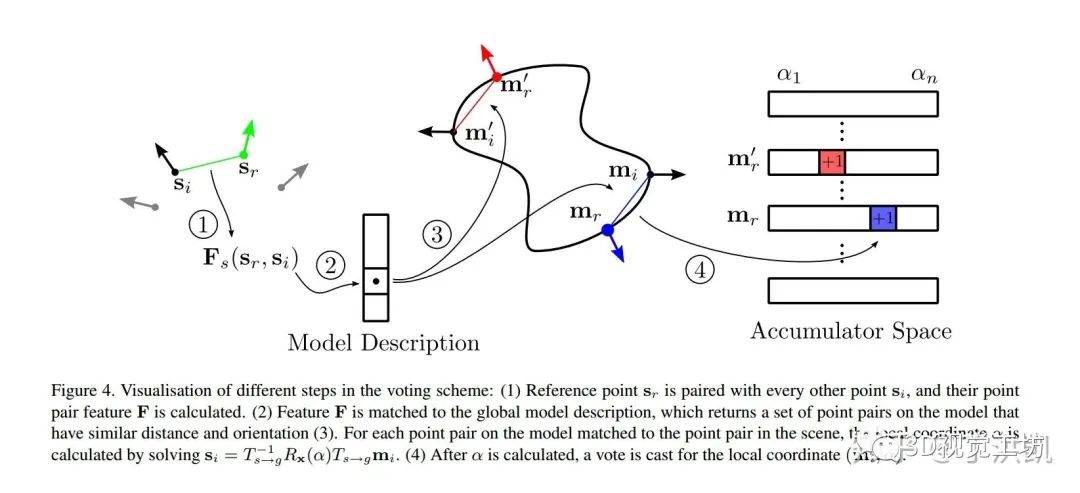
的个数。 ,与 scene 中所有其他的点组成点对
,与 scene 中所有其他的点组成点对  ,对每一个点对,计算
,对每一个点对,计算  ;
; 作为 key,搜索 global model description 的哈希表,找到与
作为 key,搜索 global model description 的哈希表,找到与  类似(distance & normal)的 model 特征矢量
类似(distance & normal)的 model 特征矢量  和点对
和点对  ;
; ,通过之前的公式
,通过之前的公式  可以算出旋转角
可以算出旋转角  ;
; 与二维数组中离散
与二维数组中离散  对应的位置投票(+1);
对应的位置投票(+1); 的最大得票所对应的
的最大得票所对应的  和
和  ,即最优的 local coordinates
,即最优的 local coordinates 
 ,为了加速计算,将
,为了加速计算,将  分解:
分解:  ,这样就可以分别计算
,这样就可以分别计算  和
和  了。
了。 和
和  ,求得:
,求得:
 都是唯一的
都是唯一的 可以在离线阶段求解
可以在离线阶段求解 只需要算一次
只需要算一次 ,保证至少有一个参考点能在物体表面。
,保证至少有一个参考点能在物体表面。二、 OpenCV 实现
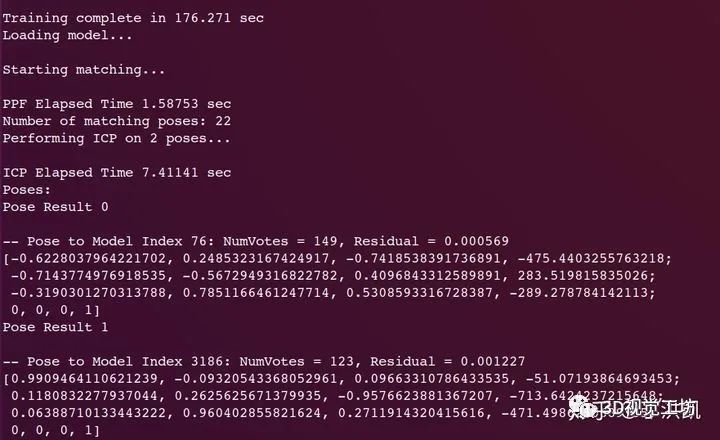
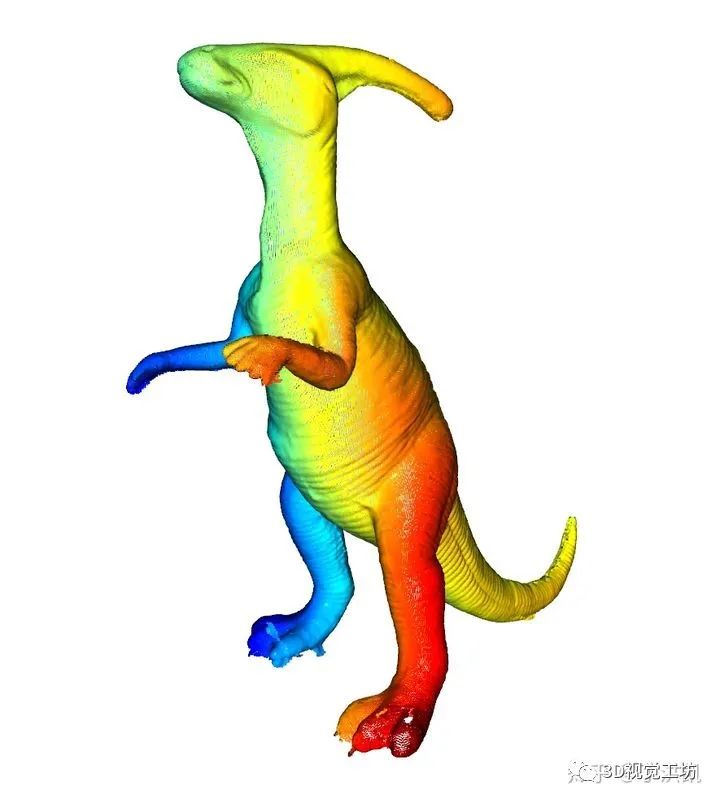

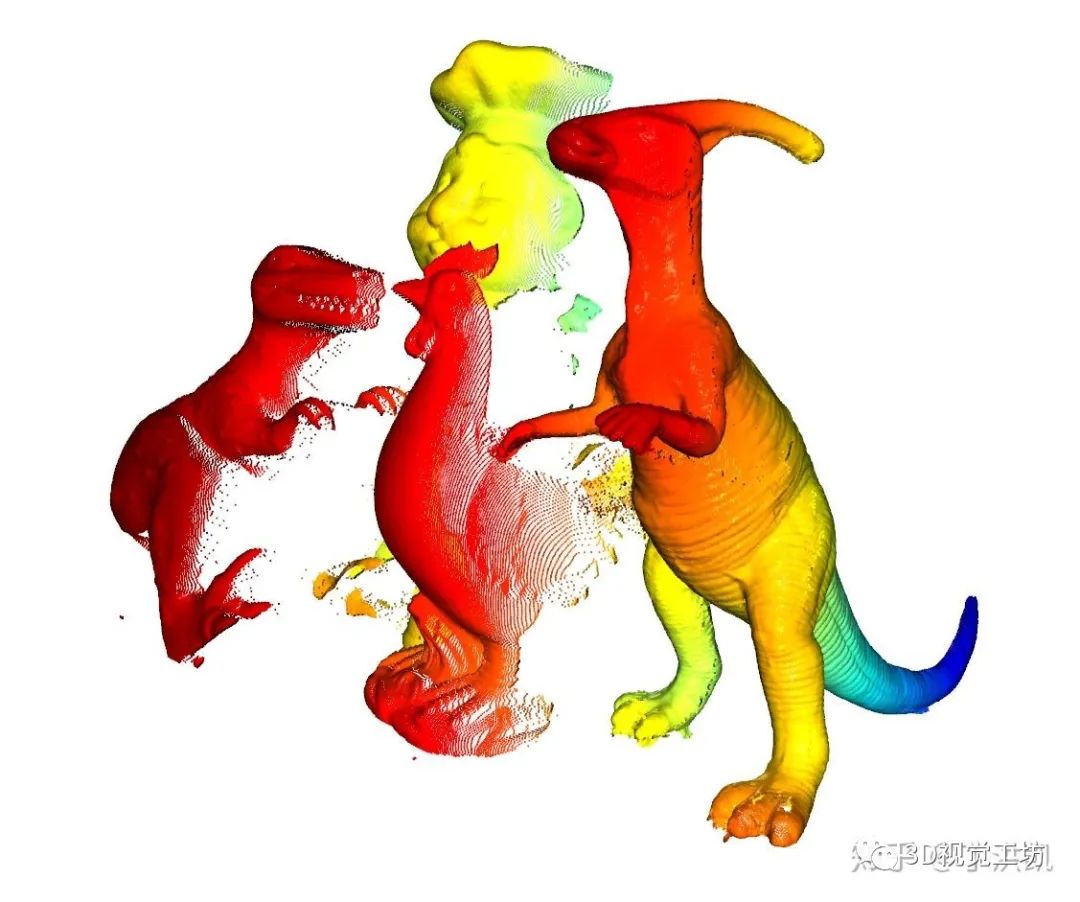
三、Matlab 实现
mex mex/computePPFmex.cpp
mex mex/computePPFmex.cpp
mex mex/MurmurHash3.cpp
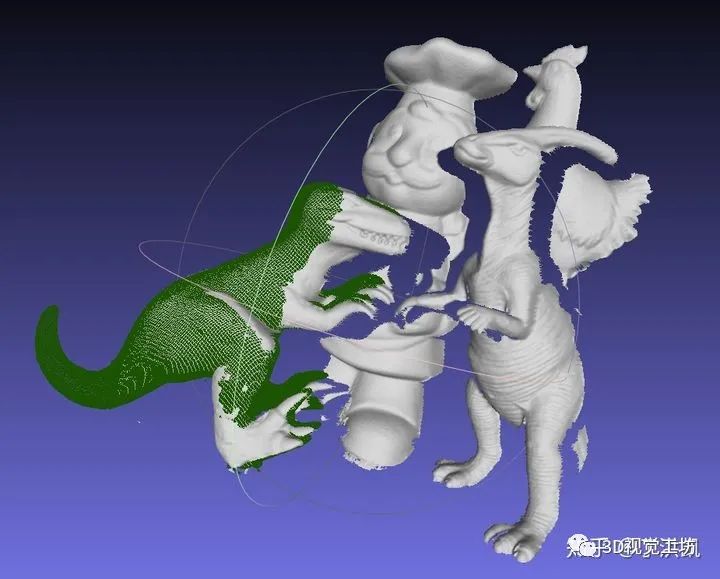
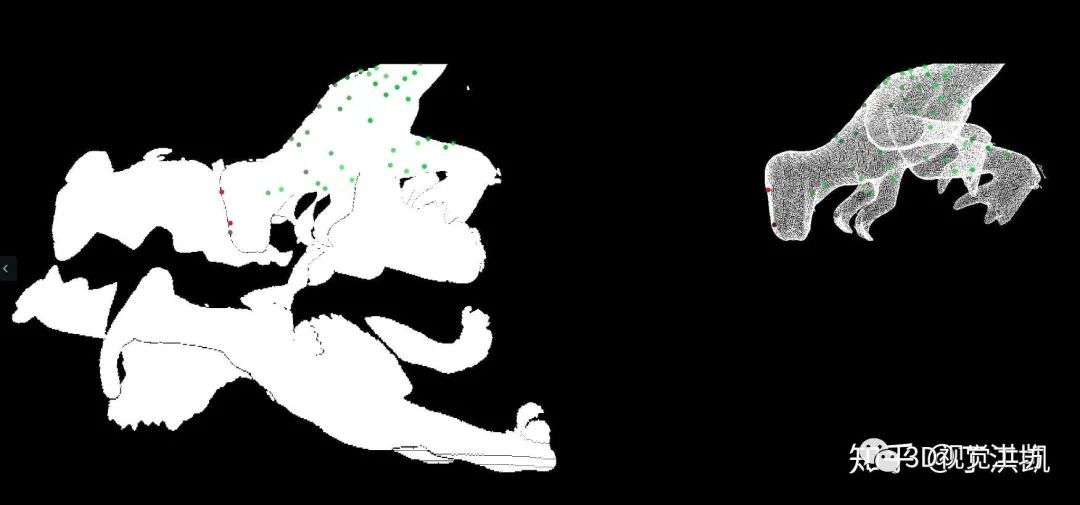




四、PCL 实现

重磅!3DCVer-学术论文写作投稿 交流群已成立
扫码添加小助手微信,可申请加入3D视觉工坊-学术论文写作与投稿 微信交流群,旨在交流顶会、顶刊、SCI、EI等写作与投稿事宜。
同时也可申请加入我们的细分方向交流群,目前主要有3D视觉、CV&深度学习、SLAM、三维重建、点云后处理、自动驾驶、多传感器融合、CV入门、三维测量、VR/AR、3D人脸识别、医疗影像、缺陷检测、行人重识别、目标跟踪、视觉产品落地、视觉竞赛、车牌识别、硬件选型、学术交流、求职交流、ORB-SLAM系列源码交流、深度估计等微信群。
一定要备注:研究方向+学校/公司+昵称,例如:”3D视觉 + 上海交大 + 静静“。请按照格式备注,可快速被通过且邀请进群。原创投稿也请联系。

▲长按加微信群或投稿 
▲长按关注公众号


▲长按关注公众号
3D视觉从入门到精通知识星球:针对3D视觉领域的视频课程(三维重建系列、三维点云系列、结构光系列、手眼标定、相机标定、orb-slam3等视频课程)、知识点汇总、入门进阶学习路线、最新paper分享、疑问解答五个方面进行深耕,更有各类大厂的算法工程人员进行技术指导。与此同时,星球将联合知名企业发布3D视觉相关算法开发岗位以及项目对接信息,打造成集技术与就业为一体的铁杆粉丝聚集区,近2000星球成员为创造更好的AI世界共同进步,知识星球入口:
学习3D视觉核心技术,扫描查看介绍,3天内无条件退款 
圈里有高质量教程资料、可答疑解惑、助你高效解决问题 觉得有用,麻烦给个赞和在看~