本文介绍3个plotly非常实用的高级操作范例:
1,绘制时间序列设置滑块;
2,绘制地图设置高德底图;
3,使用dash构建交互面板;
公众号后台回复关键词:plotly,获取本文jupyter notebook 源代码~
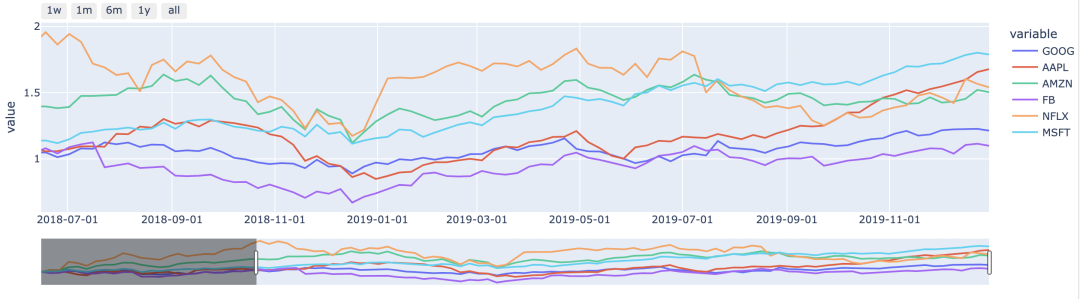
一,绘制时间序列设置滑块
可以使用一个滑块来选择绘图时间范围。
import plotly.express as px
dfdata = px.data.stocks()
fig = px.line(data_frame=dfdata, x = 'date',y = ['GOOG', 'AAPL', 'AMZN', 'FB', 'NFLX', 'MSFT'])
fig.update_xaxes(dtick="M2",tickformat="%Y-%m-%d",rangeslider=dict(visible=True),
rangeselector={'buttons': [{'count': 7,
'label': '1w',
'step': 'day',
'stepmode': 'backward'},
{'count': 1, 'label': '1m', 'step': 'month', 'stepmode': 'backward'},
{'count': 6, 'label': '6m', 'step': 'month', 'stepmode': 'backward'},
{'count': 1, 'label': '1y', 'step': 'year', 'stepmode': 'backward'},
{'step': 'all'}]}
)
fig.update_layout(#autosize=True,
#width=1000,
#height=600,
margin=dict(
r=0, t=0, l=0, b=0, pad=0)
)
fig.show()
fig.write_html('test.html')
效果如下:
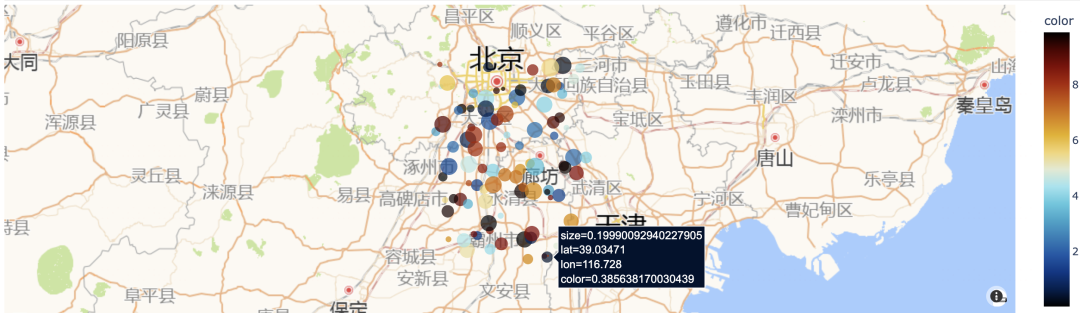
二,绘制地图设置高德底图
plotly绘制地图可以使用高德底图。
import plotly.express as px
dfdata = pd.DataFrame({'lat': 39 + np.random.rand(100),
'lon': 116+np.random.rand(100),
'color': 10*np.random.rand(100),
'size': 0.5*np.random.rand(100),
})
fig = px.scatter_mapbox(dfdata, lat="lat",
lon="lon", color="color",
size="size",
color_continuous_scale=px.colors.cyclical.IceFire,
size_max=15, zoom=10
)
basemap_layer = [
dict(
below="traces",
sourcetype="raster",
sourceattribution="高德地图",
source=[
"http://wprd01.is.autonavi.com/appmaptile?x={x}&y={y}&z={z}&lang=zh_cn&size=1&scl=1&style=7"
]
)
]
fig.update_mapboxes(style='white-bg',zoom=7,layers=basemap_layer)
fig.update_layout(margin=dict(r=0, t=0, l=0, b=0, pad=0))
fig.show()
效果如下:
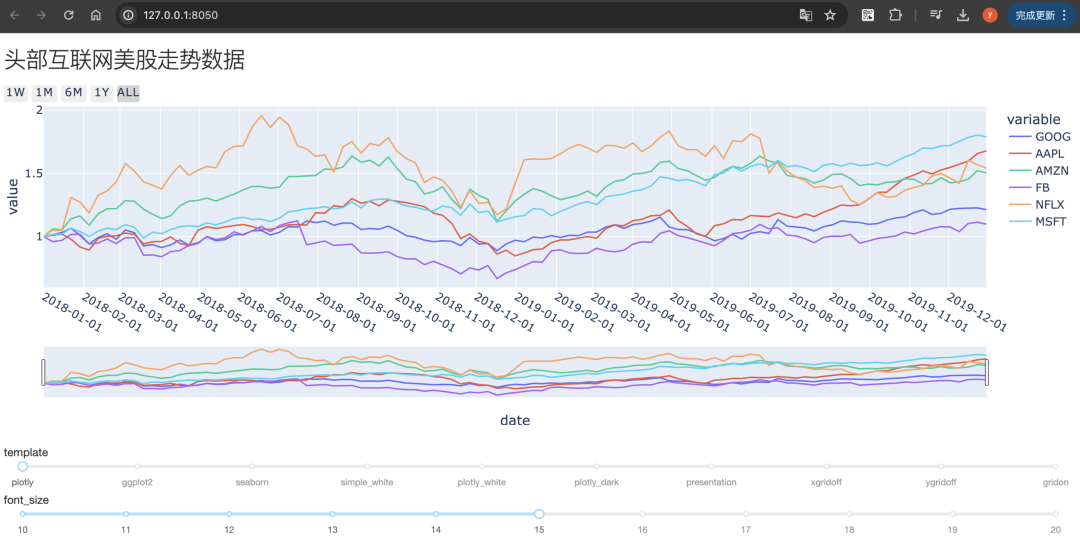
三,使用dash构建交互面板
使用plotly的dash可以让做出非常丰富的前端交互效果。
详情参考:https://dash.plotly.com/
import dash
from dash import Dash, dcc, html, Input, Output
import plotly.express as px
external_stylesheets = ['https://codepen.io/chriddyp/pen/bWLwgP.css']
template_list = ['plotly','ggplot2', 'seaborn', 'simple_white',
'plotly_white', 'plotly_dark', 'presentation', 'xgridoff',
'ygridoff', 'gridon']
# 1,生成示例数据
dfdata = px.data.stocks()
# 2, 创建Dash app
app = Dash(__name__,external_stylesheets=external_stylesheets)
# 3, 设计页面布局
app.layout = html.Div([
html.H3(children='头部互联网美股走势数据'),
dcc.Graph(id='stock-plot'),
html.Br(),
html.Label('template'),
dcc.Slider(
id='template',
min=0,
max=len(template_list)-1,
value=0,
marks={i: template_list[i] for i in range(len(template_list))},
step=1
),
html.Label('font_size'),
dcc.Slider(
id='font_size',
min=10,
max=20,
value=15,
marks={i: str(i) for i in range(10,21)},
step=1
)
])
# 4, 编写回调函数
@app.callback(
Output(component_id='stock-plot', component_property='figure'),
[Input(component_id='template', component_property='value'),
Input(component_id='font_size', component_property='value')
]
)
def update_figure(template,font_size):
fig = px.line(data_frame=dfdata, x = 'date',y = ['GOOG', 'AAPL', 'AMZN', 'FB', 'NFLX', 'MSFT'])
fig.update_xaxes(dtick="M1",tickformat="%Y-%m-%d",rangeslider=dict(visible=True),
rangeselector={'buttons': [{'count': 7,
'label': '1w',
'step': 'day',
'stepmode': 'backward'},
{'count': 1, 'label': '1m', 'step': 'month', 'stepmode': 'backward'},
{'count': 6, 'label': '6m', 'step': 'month', 'stepmode': 'backward'},
{'count': 1, 'label': '1y', 'step': 'year', 'stepmode': 'backward'},
{'step': 'all'}]}
)
fig.layout.template = template_list[template]
fig.update_layout(autosize=True,
#width=1000,
#height=600,
margin=dict(
r=0, t=0, l=0, b=0, pad=0)
)
fig.update_layout({"font.size":font_size})
return fig
# 5, 运行交互页面
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
#app.run(jupyter_mode="tab") #'inline', 'external', 'jupyterlab', 'tab'
运行上述代码,会弹出一个可以交互的网页,效果如下:
猜你喜欢: