👇我的小册 40章教程:( 小白零基础用Python量化股票分析小册 ) ,原价299,限时特价2杯咖啡,满100人涨10元。
作者:Nirmalya Ghosh 来源:deephub 转自:数据STUDIO
在本文中,我将介绍一些简单的方法,可以将Python for循环的速度提高1.3到900倍。
Python内建的一个常用功能是timeit模块。下面几节中我们将使用它来度量循环的当前性能和改进后的性能。
对于每种方法,我们通过运行测试来建立基线,该测试包括在10次测试运行中运行被测函数100K次(循环),然后计算每个循环的平均时间(以纳秒为单位,ns)。
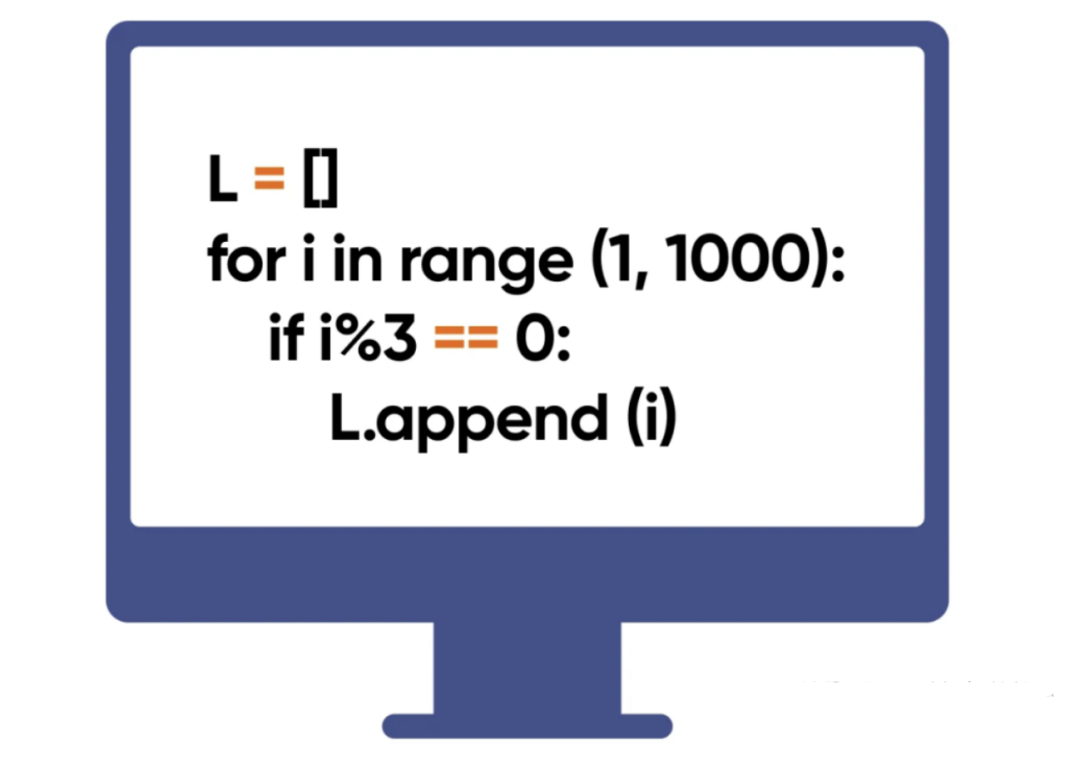
几个简单方法
1、列表推导式
# Baseline version (Inefficient way)
# Calculating the power of numbers
# Without using List Comprehension
def test_01_v0(numbers):
output = []
for n in numbers:
output.append(n ** 2.5)
return output
# Improved version
# (Using List Comprehension)
def test_01_v1(numbers):
output = [n ** 2.5 for n in numbers]
return output
结果如下:
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 32.158 ns per loop
Improved: 16.040 ns per loop
% Improvement: 50.1 %
Speedup: 2.00x
可以看到使用列表推导式可以得到2倍速的提高
2、在外部计算长度
如果需要依靠列表的长度进行迭代,请在for循环之外进行计算。
# Baseline version (Inefficient way)
# (Length calculation inside for loop)
def test_02_v0(numbers):
output_list = []
for i in range(len(numbers)):
output_list.append(i * 2)
return output_list
# Improved version
# (Length calculation outside for loop)
def test_02_v1(numbers):
my_list_length = len(numbers)
output_list = []
for i in range(my_list_length):
output_list.append(i * 2)
return output_list
通过将列表长度计算移出for循环,加速1.6倍,这个方法可能很少有人知道吧。
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 112.135 ns per loop
Improved: 68.304 ns per loop
% Improvement: 39.1 %
Speedup: 1.64x
3、使用Set
在使用for循环进行比较的情况下使用set。
# Use for loops for nested lookups
def test_03_v0(list_1, list_2):
# Baseline version (Inefficient way)
# (nested lookups using for loop)
common_items = []
for item in list_1:
if item in list_2:
common_items.append(item)
return common_items
def test_03_v1(list_1, list_2):
# Improved version
# (sets to replace nested lookups)
s_1 = set(list_1)
s_2 = set(list_2)
output_list = []
common_items = s_1.intersection(s_2)
return common_items
在使用嵌套for循环进行比较的情况下,使用set加速498x
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 9047.078 ns per loop
Improved: 18.161 ns per loop
% Improvement: 99.8 %
Speedup: 498.17x
4、跳过不相关的迭代
避免冗余计算,即跳过不相关的迭代。
# Example of inefficient code used to find
# the first even square in a list of numbers
def function_do_something(numbers):
for n in numbers:
square = n * n
if square % 2 == 0:
return square
return None # No even square found
# Example of improved code that
# finds result without redundant computations
def function_do_something_v1(numbers):
even_numbers = [i for n in numbers if n%2==0]
for n in even_numbers:
square = n * n
return square
return None # No even square found
这个方法要在设计for循环内容的时候进行代码设计,具体能提升多少可能根据实际情况不同:
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 16.912 ns per loop
Improved: 8.697 ns per loop
% Improvement: 48.6 %
Speedup: 1.94x
5、代码合并
在某些情况下,直接将简单函数的代码合并到循环中可以提高代码的紧凑性和执行速度。
# Example of inefficient code
# Loop that calls the is_prime function n times.
def is_prime(n):
if n <= 1:
return False
for i in range(2, int(n**0.5) + 1):
if n % i == 0:
return False
return True
def test_05_v0(n):
# Baseline version (Inefficient way)
# (calls the is_prime function n times)
count = 0
for i in range(2, n + 1):
if is_prime(i):
count += 1
return count
def test_05_v1(n):
# Improved version
# (inlines the logic of the is_prime function)
count = 0
for i in range(2, n + 1):
if i <= 1:
continue
for j in range(2, int(i**0.5) + 1):
if i % j == 0:
break
else:
count += 1
return count
这样也可以提高1.3倍
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 1271.188 ns per loop
Improved: 939.603 ns per loop
% Improvement: 26.1 %
Speedup: 1.35x
这是为什么呢?
调用函数涉及开销,例如在堆栈上推入和弹出变量、函数查找和参数传递。当一个简单的函数在循环中被重复调用时,函数调用的开销会增加并影响性能。所以将函数的代码直接内联到循环中可以消除这种开销,从而可能显著提高速度。
⚠️但是这里需要注意,平衡代码可读性和函数调用的频率是一个要考虑的问题。
一些小技巧
6 .避免重复
考虑避免重复计算,其中一些计算可能是多余的,并且会减慢代码的速度。相反,在适用的情况下考虑预计算。
def test_07_v0(n):
# Example of inefficient code
# Repetitive calculation within nested loop
result = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
result += i * j
return result
def test_07_v1(n):
# Example of improved code
# Utilize precomputed values to help speedup
pv = [[i * j for j in range(n)] for i in range(n)]
result = 0
for i in range(n):
result += sum(pv[i][:i+1])
return result
结果如下
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 139.146 ns per loop
Improved: 92.325 ns per loop
% Improvement: 33.6 %
Speedup: 1.51x
7、使用Generators
生成器支持延迟求值,也就是说,只有当你向它请求下一个值时,里面的表达式才会被求值,动态处理数据有助于减少内存使用并提高性能。尤其是大型数据集中
def test_08_v0(n):
# Baseline version (Inefficient way)
# (Inefficiently calculates the nth Fibonacci
# number using a list)
if n <= 1:
return n
f_list = [0, 1]
for i in range(2, n + 1):
f_list.append(f_list[i - 1] + f_list[i - 2])
return f_list[n]
def test_08_v1(n):
# Improved version
# (Efficiently calculates the nth Fibonacci
# number using a generator)
a, b = 0, 1
for _ in range(n):
yield a
a, b = b, a + b
可以看到提升很明显:
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 0.083 ns per loop
Improved: 0.004 ns per loop
% Improvement: 95.5 %
Speedup: 22.06x
8、map()函数
使用Python内置的map()函数。它允许在不使用显式for循环的情况下处理和转换可迭代对象中的所有项。
def some_function_X(x):
# This would normally be a function containing application logic
# which required it to be made into a separate function
# (for the purpose of this test, just calculate and return the square)
return x**2
def test_09_v0(numbers):
# Baseline version (Inefficient way)
output = []
for i in numbers:
output.append(some_function_X(i))
return output
def test_09_v1(numbers):
# Improved version
# (Using Python's built-in map() function)
output = map(some_function_X, numbers)
return output
使用Python内置的map()函数代替显式的for循环加速了970x。
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 4.402 ns per loop
Improved: 0.005 ns per loop
% Improvement: 99.9 %
Speedup: 970.69x
这是为什么呢?
map()函数是用C语言编写的,并且经过了高度优化,因此它的内部隐含循环比常规的Python for循环要高效得多。因此速度加快了,或者可以说Python还是太慢,哈。
9、使用Memoization
记忆优化算法的思想是缓存(或“记忆”)昂贵的函数调用的结果,并在出现相同的输入时返回它们。它可以减少冗余计算,加快程序速度。
首先是低效的版本。
# Example of inefficient code
def fibonacci(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
elif n == 1:
return 1
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n-2)
def test_10_v0(list_of_numbers):
output = []
for i in numbers:
output.append(fibonacci(i))
return output
然后我们使用Python的内置functools的lru_cache函数。
# Example of efficient code
# Using Python's functools' lru_cache function
import functools
@functools.lru_cache()
def fibonacci_v2(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
elif n == 1:
return 1
return fibonacci_v2(n - 1) + fibonacci_v2(n-2)
def _test_10_v1(numbers):
output = []
for i in numbers:
output.append(fibonacci_v2(i))
return output
结果如下:
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 63.664 ns per loop
Improved: 1.104 ns per loop
% Improvement: 98.3 %
Speedup: 57.69x
使用Python的内置functools的lru_cache函数使用Memoization加速57x。
lru_cache函数是如何实现的?
“LRU”是“Least Recently Used”的缩写。lru_cache是一个装饰器,可以应用于函数以启用memoization。它将最近函数调用的结果存储在缓存中,当再次出现相同的输入时,可以提供缓存的结果,从而节省了计算时间。lru_cache函数,当作为装饰器应用时,允许一个可选的maxsize参数,maxsize参数决定了缓存的最大大小(即,它为多少个不同的输入值存储结果)。如果maxsize参数设置为None,则禁用LRU特性,缓存可以不受约束地增长,这会消耗很多的内存。这是最简单的空间换时间的优化方法。
10、向量化
import numpy as np
def test_11_v0(n):
# Baseline version
# (Inefficient way of summing numbers in a range)
output = 0
for i in range(0, n):
output = output + i
return output
def test_11_v1(n):
# Improved version
# (# Efficient way of summing numbers in a range)
output = np.sum(np.arange(n))
return output
向量化一般用于机器学习的数据处理库numpy和pandas
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 32.936 ns per loop
Improved: 1.171 ns per loop
% Improvement: 96.4 %
Speedup: 28.13x
11、避免创建中间列表
使用filterfalse可以避免创建中间列表。它有助于使用更少的内存。
def test_12_v0(numbers):
# Baseline version (Inefficient way)
filtered_data = []
for i in numbers:
filtered_data.extend(list(
filter(lambda x: x % 5 == 0,
range(1, i**2))))
return filtered_data
使用Python的内置itertools的filterfalse函数实现相同功能的改进版本。
from itertools import filterfalse
def test_12_v1(numbers):
# Improved version
# (using filterfalse)
filtered_data = []
for i in numbers:
filtered_data.extend(list(
filterfalse(lambda x: x % 5 != 0,
range(1, i**2))))
return filtered_data
这个方法根据用例的不同,执行速度可能没有显著提高,但通过避免创建中间列表可以降低内存使用。我们这里获得了131倍的提高
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 333167.790 ns per loop
Improved: 2541.850 ns per loop
% Improvement: 99.2 %
Speedup: 131.07x
12、高效连接字符串
任何使用+操作符的字符串连接操作都会很慢,并且会消耗更多内存。使用join代替。
def test_13_v0(l_strings):
# Baseline version (Inefficient way)
# (concatenation using the += operator)
output = ""
for a_str in l_strings:
output += a_str
return output
def test_13_v1(numbers):
# Improved version
# (using join)
output_list = []
for a_str in l_strings:
output_list.append(a_str)
return "".join(output_list)
该测试需要一种简单的方法来生成一个较大的字符串列表,所以写了一个简单的辅助函数来生成运行测试所需的字符串列表。
from faker import Faker
def generate_fake_names(count : int=10000):
# Helper function used to generate a
# large-ish list of names
fake = Faker()
output_list = []
for _ in range(count):
output_list.append(fake.name())
return output_list
l_strings = generate_fake_names(count=50000)
结果如下:
# Summary Of Test Results
Baseline: 32.423 ns per loop
Improved: 21.051 ns per loop
% Improvement: 35.1 %
Speedup: 1.54x
使用连接函数而不是使用+运算符加速1.5倍。为什么连接函数更快?
使用+操作符的字符串连接操作的时间复杂度为O(n²),而使用join函数的字符串连接操作的时间复杂度为O(n)。
总结
本文介绍了一些简单的方法,将Python for循环的提升了1.3到970x。
- 使用Python内置的map()函数代替显式的for循环加速970x
- 使用set代替嵌套的for循环加速498x[技巧#3]
- 使用itertools的filterfalse函数加速131x
- 使用lru_cache函数使用Memoization加速57x

最后推荐一下我们团队写的量化小册的内容 ,45篇内容 !从Python安装,入门,数据分析,爬取股票基金的历史+实时数据,以及如何写一个简单量化策略,策略回测,如何看资金曲线统统都有介绍!非常超值!
欢迎订阅: 原价 199 早鸟价2杯咖啡钱,即可永久阅读。满400人又要涨价了,现在的价格非常非常低, 只要2杯奶茶,就可以终身订阅+课程源码 ,还有永久陪伴群。48小时无理由退款,放心食用!
往期推荐
量化: 如何用Python爬取创业板历史+实时股票数据!|实战股票分析篇利用Pandas 9招挖掘五粮液股价!|实战股票数据分析篇 Pandas滚动操作 |量化股票第一步,用Python画股票K线,双均线图,可视化你的股票数据!|如何用Python爬取全部800多只ETF基金数据!|如何用Python写一个双均线策略 |如何用Python开发一个多策略机器人!上篇!|Python量化系列-用布林策略买五粮液能赚多少钱?|只要4秒钟!用Python 获取上证指数34年的历史日线数据!
入门: 最全的零基础学Python的问题 | 零基础学了8个月的Python | 实战项目 |学Python就是这条捷径
干货:爬取豆瓣短评,电影《后来的我们》 | 38年NBA最佳球员分析 | 从万众期待到口碑扑街!唐探3令人失望 | 笑看新倚天屠龙记 | 灯谜答题王 |用Python做个海量小姐姐素描图 |碟中谍这么火,我用机器学习做个迷你推荐系统电影
趣味:弹球游戏 | 九宫格 | 漂亮的花 | 两百行Python《天天酷跑》游戏!
AI: 会做诗的机器人 | 给图片上色 | 预测收入 | 碟中谍这么火,我用机器学习做个迷你推荐系统电影
小工具: Pdf转Word,轻松搞定表格和水印! | 一键把html网页保存为pdf! | 再见PDF提取收费! | 用90行代码打造最强PDF转换器,word、PPT、excel、markdown、html一键转换 | 制作一款钉钉低价机票提示器! | 60行代码做了一个语音壁纸切换器天天看小姐姐!|