Seata是Spring Cloud Alibaba中一款开源的分布式事务解决方案,本文具体就Seata的TCC 模式进行介绍、实践

环境配置
基础环境
首先通过Docker Compose搭建基础环境——Nacos、MySQL服务,具体如下
# Compose 版本
version: '3.8'
# 定义Docker服务
services:
# Nacos 服务
Nacos-Service-1:
image: nacos/nacos-server:1.4.2
container_name: Nacos-Service-1
ports:
- "9848:8848"
environment:
MODE: standalone
networks:
seata_tcc_net:
ipv4_address: 130.130.130.32
# MySQL 服务 (用于PayService)
PayService-DB:
image: mysql:5.7
container_name: PayService-DB
ports:
- "9306:3306"
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: 12345
networks:
seata_tcc_net:
ipv4_address: 130.130.130.36
# MySQL 服务 (用于StorageService)
StorageService-DB:
image: mysql:5.7
container_name: StorageService-DB
ports:
- "9307:3306"
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: 12345
networks:
seata_tcc_net:
ipv4_address: 130.130.130.37
# 定义网络
networks:
seata_tcc_net:
ipam:
config:
- subnet: 130.130.130.0/24
配置Seata Server
通过Github下载Seata Server,命令如下
wget https://github.com/seata/seata/releases/download/v1.3.0/seata-server-1.3.0.zip
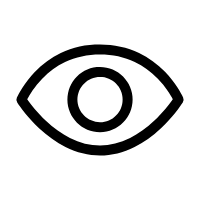
修改Seata Server下conf目录的registry.conf文件,将注册中心、配置中心均设置Nacos。需要注意的是如果没有logs目录,则需要手动创建该目录
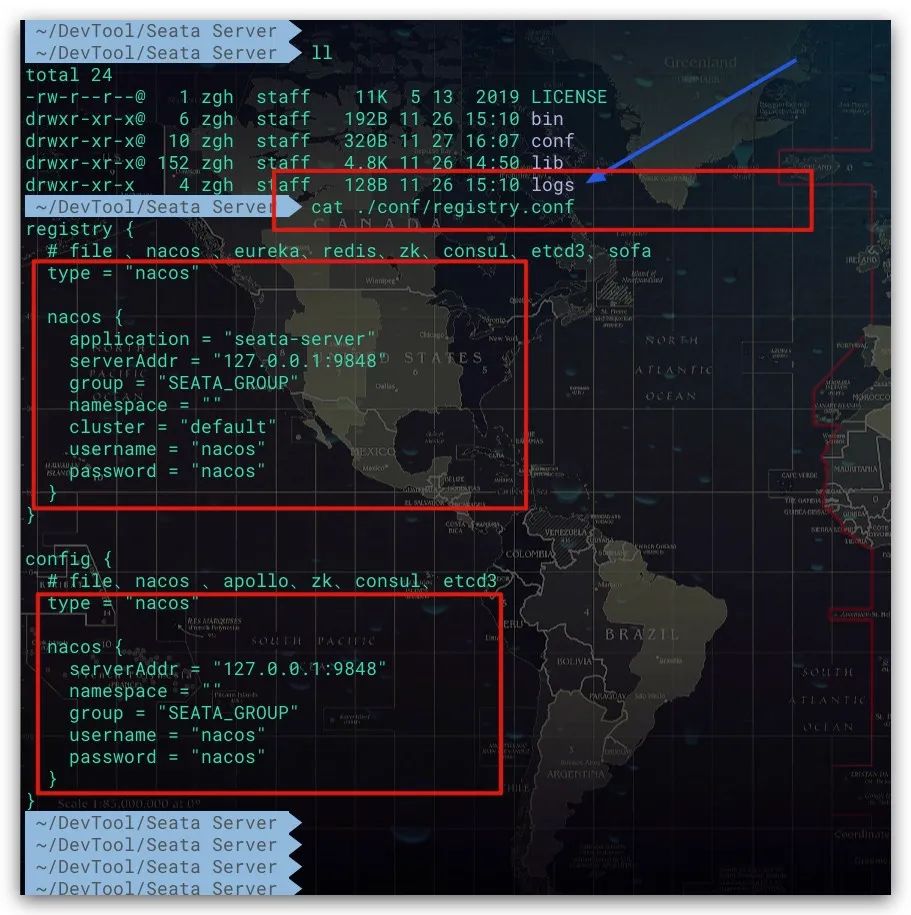
对于Seata Server而言,其配置信息支持两种形式:本地文件、配置中心。对于后者而言,我们需要将Seata的相关配置项导入到配置中心。同样,我们需要通过Github来下载配置文件config.txt及相应的导入脚本nacos-config.sh
# 下载地址: 配置中心的配置项
https://github.com/seata/seata/blob/1.3.0/script/config-center/config.txt
# 下载地址: 用于将配置项导入至Nacos的脚本
https://github.com/seata/seata/blob/1.3.0/script/config-center/nacos/nacos-config.sh
在通过Shell脚本导入配置至Nacos过程中,配置文件config.txt应与Shell脚本的上一级目录保持平行。然后在Shell脚本所在目录中执行如下命令即可
# 执行Shell脚本
sh nacos-config.sh -h localhost -p 9848
该Shell脚本支持的选项如下所示
-h: Nacos服务的IP地址,默认为localhost -p: Nacos服务的Port端口,默认为8848 -g: Nacos分组名,默认为SEATA_GROUP -t: Nacos命名空间ID。默认为"",即使用public命名空间 -u: Nacos服务的用户名 -w: Nacos服务的密码
效果如下所示
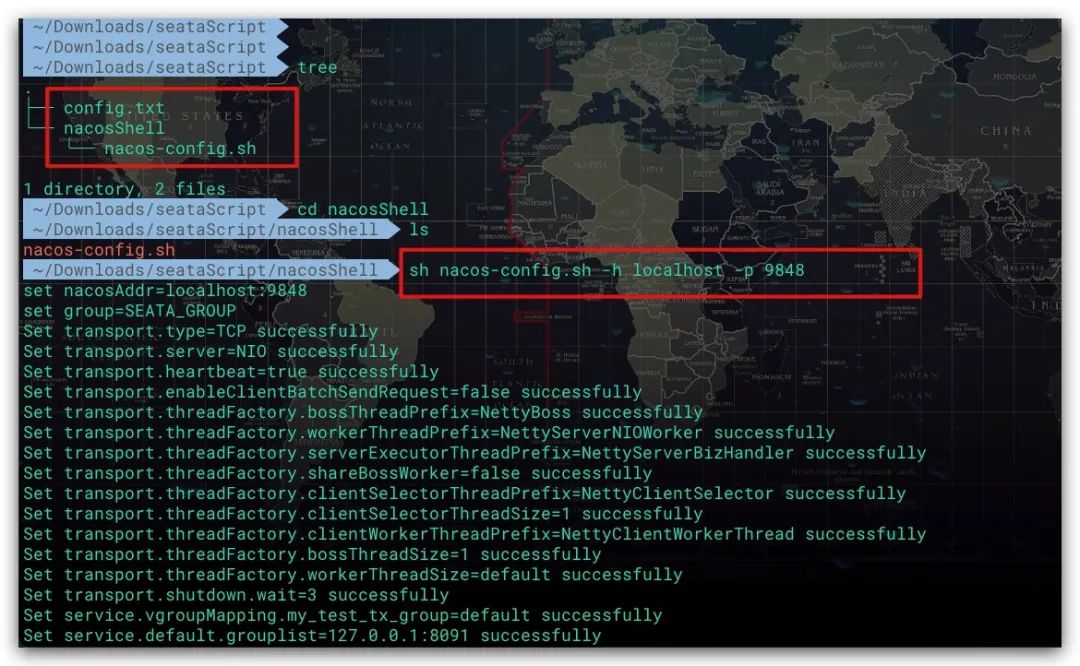
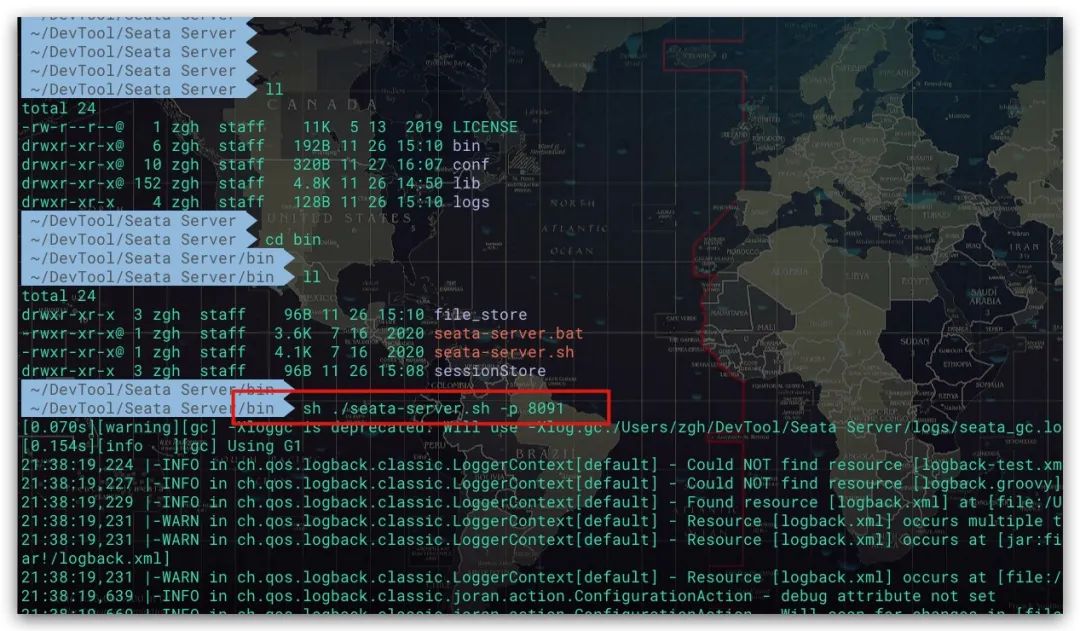
至此Seata Server相关环境及配置就完成了,只需通过Seata Server下bin目录的seata-server.sh脚本启动服务即可。其中-p选项指定服务使用的端口,默认为8091
搭建库存服务
POM依赖
通过SpringBoot搭建库存服务StorageService。这里给出关键性的依赖及版本,如下所示
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!--Spring Boot-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!--Spring Cloud-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Hoxton.SR8</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!--Spring Cloud Alibaba-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.3.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!--Spring Cloud Alibaba Seata -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seata</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--Seata版本与Seata Server保持一致-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos Discovery -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.76</version>
</dependency>
<!--Mybatis Plus-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
服务配置
该服务的配置文件如下所示
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
name: StorageService
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:9307/StorageDb?allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 12345
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
# 注册中心 Nacos 地址信息
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:9848
alibaba:
seata:
# 配置使用的事务分组名称
tx-service-group: my_test_tx_group
# Mybatis-Plus 配置
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
# Seata Server配置
seata:
# Seata服务端所在注册中心的配置信息
registry:
# 注册中心类型
type: nacos
nacos:
# Seata服务端的服务名
application: seata-server
# Seata服务端所在的注册中心信息
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:9848
username: nacos
password: nacos
group: SEATA_GROUP
# Seata服务端所在配置中心的配置信息
config:
type: nacos
nacos:
# Seata服务端所在的配置中心信息
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:9848
username: nacos
password: nacos
group: SEATA_GROUP
# 使能Seata自动代理数据源
enable-auto-data-source-proxy: true
# Actuator配置: 开启所有端点
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
base-path: /actuator
服务实现
这里直接添加一个Controller类用以实现库存扣减,核心代码实现如下
@RestController
@RequestMapping("goods")
@Slf4j
public class GoodsController {
@Autowired
private GoodsStorageService goodsStorageService;
@RequestMapping("/sell")
public String sell(@RequestBody GoodsDto goodsDto) {
String msg = "success";
goodsStorageService.sell(null, goodsDto);
return msg;
}
}
...
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class GoodsDto {
/**
* 商品名
*/
private String goodsName;
/**
* 数量
*/
private int num;
}
作为TCC的分布式事务方案来说,对于一个售卖商品扣减库存的过程。需要根据Try-Confirm-Cancel的设计要求,将库存的扣减分为两阶段完成。首先在GoodsStorageService接口中定义sell、confirmSell、cancelSell方法,然后在接口上添加@LocalTCC注解,最后在Try方法上添加@TwoPhaseBusinessAction注解。具体地,@TwoPhaseBusinessAction注解的name属性只需保证唯一性即可、commitMethod/rollbackMethod属性用来设置两阶段调用的方法名。TCC中各方法的BusinessActionContext参数是TCC两阶段之间用来传递参数的context上下文,故在Controller中调用Try方法时BusinessActionContext参数只需传null值即可。并将通过@BusinessActionContextParameter注解将相关参数以指定名称存入context上下文。与此同时还在接口中提供了一个默认方法getParamByContext,以便于二阶段时从context上下文获取参数。为了保证TCC二阶段的Confirm、Cancel接口的幂等性,这里在实现类中通过向resultHolder存入xid全局事务ID进行幂等控制
@LocalTCC
public interface GoodsStorageService {
/**
* 定义context中参数名
*/
String paramName = "params";
/**
* 从context中获取指定参数名所对应的值
* @param context
* @return
*/
default GoodsDto getParamByContext(BusinessActionContext context) {
JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) context.getActionContext(paramName);
GoodsDto goodsDto = jsonObject.toJavaObject(GoodsDto.class);
return goodsDto;
}
/**
* Try方法: 售卖
* @param goodsDto
* @return
*/
@TwoPhaseBusinessAction(name = "sell", commitMethod = "confirmSell", rollbackMethod = "cancelSell")
int sell(BusinessActionContext context,
@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = paramName) GoodsDto goodsDto);
/**
* Confirm方法: 确认售卖
* @param context
* @return
*/
void confirmSell(BusinessActionContext context);
/**
* Cancel方法: 取消售卖
* @param context
* @return
*/
void cancelSell(BusinessActionContext context);
}
...
@Service
@Slf4j
public class GoodsStorageServiceImpl implements GoodsStorageService {
private static Set<String> resultHolder = new ConcurrentHashSet<>();
@Autowired
private GoodsStorageMapper goodsStorageMapper;
@Override
public int sell(BusinessActionContext context, GoodsDto goodsDto) {
// 获取全局事务ID
String xid = context.getXid();
int result = goodsStorageMapper.sell(goodsDto);
log.info("[Goods Storage Service]: result: {}", result);
if( result != 1 ) {
throw new RuntimeException("商品库存不足");
}
resultHolder.add( xid );
return result;
}
@Override
public void confirmSell(BusinessActionContext context) {
// 获取全局事务ID
String xid = context.getXid();
// 幂等设计: 防止重复提交
if( !resultHolder.contains(xid) ) {
return;
}
GoodsDto goodsDto = getParamByContext(context);
goodsStorageMapper.confirmSell(goodsDto);
resultHolder.remove(xid);
log.info("[Goods Storage Service]: confirm sell");
}
@Override
public void cancelSell(BusinessActionContext context) {
// 获取全局事务ID
String xid = context.getXid();
// 1. 幂等设计: 防止重复回滚; 2. 实现空回滚
if( !resultHolder.contains(xid) ) {
return;
}
GoodsDto goodsDto = getParamByContext(context);
goodsStorageMapper.cancelSell(goodsDto);
resultHolder.remove(xid);
log.info("[Goods Storage Service]: cancel sell");
}
}
DB层面
商品库存表对应的实体类GoodsStorage如下所示
/**
* 商品库存
*/
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@TableName("goods_storage")
public class GoodsStorage {
@TableId
private int id;
/**
* 商品名
*/
private String goodsName;
/**
* 可用库存数
*/
private int stock;
/**
* 售出数
*/
private int soldNum;
/**
* 冻结库存数
*/
private int freezeNum;
}
而售卖商品扣减库存的各阶段方法所使用的SQL如下所示,至此就可以明白freezeNum冻结库存数这一中间状态的含义。这也是TCC方案两阶段的具体体现
<update id="sell" parameterType="com.aaron.StorageService.dto.GoodsDto">
update goods_storage
set stock = stock - #{num}, freeze_num = freeze_num + #{num}
where goods_name = #{goodsName}
and (stock - #{num}) >= 0
</update>
<update id="confirmSell" parameterType="com.aaron.StorageService.dto.GoodsDto">
update goods_storage
set sold_num = sold_num + #{num}, freeze_num = freeze_num - #{num}
where goods_name = #{goodsName}
</update>
<update id="cancelSell" parameterType="com.aaron.StorageService.dto.GoodsDto">
update goods_storage
set stock = stock + #{num}, freeze_num = freeze_num - #{num}
where goods_name = #{goodsName}
</update>
搭建支付服务
为了验证分布式事务,自然不能只有一个微服务。故这里类似地我们再搭建一个PayService支付服务。当然基本搭建过程与StorageService服务并无明显差异。首先在POM依赖方面,PayService服务的POM依赖与StorageService服务一致,同样也需要引入Seata、Nacos等相关依赖。其次在服务配置方面,PayService服务的application.yml配置文件中关于Seata、Nacos相关的配置自然与StorageService服务并无二致。但需调整修改其所连接的数据库信息,部分配置如下所示
server:
port: 90
spring:
application:
name: PayService
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:9306/PayDb?allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 12345
这里添加一个Controller用于进行余额、库存的扣减。作为分布式事务的发起者,这里需要添加一个@GlobalTransactional注解
@RestController
@RequestMapping("pay")
@Slf4j
public class PayController {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Autowired
private PayService payService;
@GlobalTransactional
@RequestMapping("/buy")
public String buy() {
// 1. 扣余额
PayDto payDto = new PayDto("Aaron",2000);
payService.pay(null, payDto);
// 2. 扣库存
String url = "http://StorageService/goods/sell";
GoodsDto goodsDto = new GoodsDto("iPhone", 5);
String response = restTemplate.postForObject(url, goodsDto, String.class);
return "complete";
}
}
...
@Configuration
public class RestTemplateConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
...
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class PayDto {
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 金额
*/
private int money;
}
类似地,Service层同样按照TCC的设计原则进行设计
@LocalTCC
public interface PayService {
/**
* 定义context中参数名
*/
String paramName = "params";
/**
* 从context中获取指定参数名所对应的值
* @param context
* @return
*/
default PayDto getParamByContext(BusinessActionContext context) {
JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) context.getActionContext(paramName);
PayDto payDto = jsonObject.toJavaObject(PayDto.class);
return payDto;
}
/**
* 会员进行支付
* @param payDto
* @return
*/
@TwoPhaseBusinessAction(name = "pay", commitMethod = "confirmPay", rollbackMethod = "cancelPay")
int pay(BusinessActionContext context,
@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = paramName) PayDto payDto );
/**
* 确认支付
* @param context
* @return
*/
void confirmPay(BusinessActionContext context);
/**
* 取消支付
* @param context
* @return
*/
void cancelPay(BusinessActionContext context);
}
...
@Service
@Slf4j
public class PayServiceImpl implements PayService {
private static Set<String> resultHolder = new ConcurrentHashSet<>();
@Autowired
private PayMapper payMapper;
@Override
public int pay(BusinessActionContext context, PayDto payDto) {
// 获取全局事务ID
String xid = context.getXid();
int result = payMapper.pay(payDto);
log.info("[Pay Service]: result: {}", result);
if( result != 1 ) {
throw new RuntimeException("账户余额不足");
}
resultHolder.add( xid );
return result;
}
@Override
public void confirmPay(BusinessActionContext context) {
// 获取全局事务ID
String xid = context.getXid();
// 幂等设计: 防止重复提交
if( !resultHolder.contains(xid) ) {
return;
}
PayDto payDto = getParamByContext(context);
payMapper.confirmPay( payDto );
resultHolder.remove(xid);
log.info("[Pay Service]: confirm pay");
}
@Override
public void cancelPay(BusinessActionContext context) {
// 获取全局事务ID
String xid = context.getXid();
// 1. 幂等设计: 防止重复回滚; 2. 实现空回滚
if( !resultHolder.contains(xid) ) {
return;
}
PayDto payDto = getParamByContext(context);
payMapper.cancelPay( payDto );
resultHolder.remove(xid);
log.info("[Pay Service]: cancel pay");
}
}
余额表对应的实体类Pay如下所示
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@TableName("member_balance")
public class Pay {
@TableId
private int id;
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 余额
*/
private int balance;
/**
* 冻结金额
*/
private int freeze;
}
而支付的各阶段方法所使用的SQL如下所示,其同样通过中间状态freeze冻结金额这一中间状态实现TCC的两阶段
<update id="pay" parameterType="com.aaron.PayService.dto.PayDto">
update member_balance
set balance = balance - #{money}, freeze = freeze + #{money}
where name = #{name}
and (balance - #{money}) >= 0
</update>
<update id="confirmPay" parameterType="com.aaron.PayService.dto.PayDto">
update member_balance
set freeze = freeze - #{money}
where name = #{name}
</update>
<update id="cancelPay" parameterType="com.aaron.PayService.dto.PayDto">
update member_balance
set balance = balance + #{money}, freeze = freeze - #{money}
where name = #{name}
</update>
测试
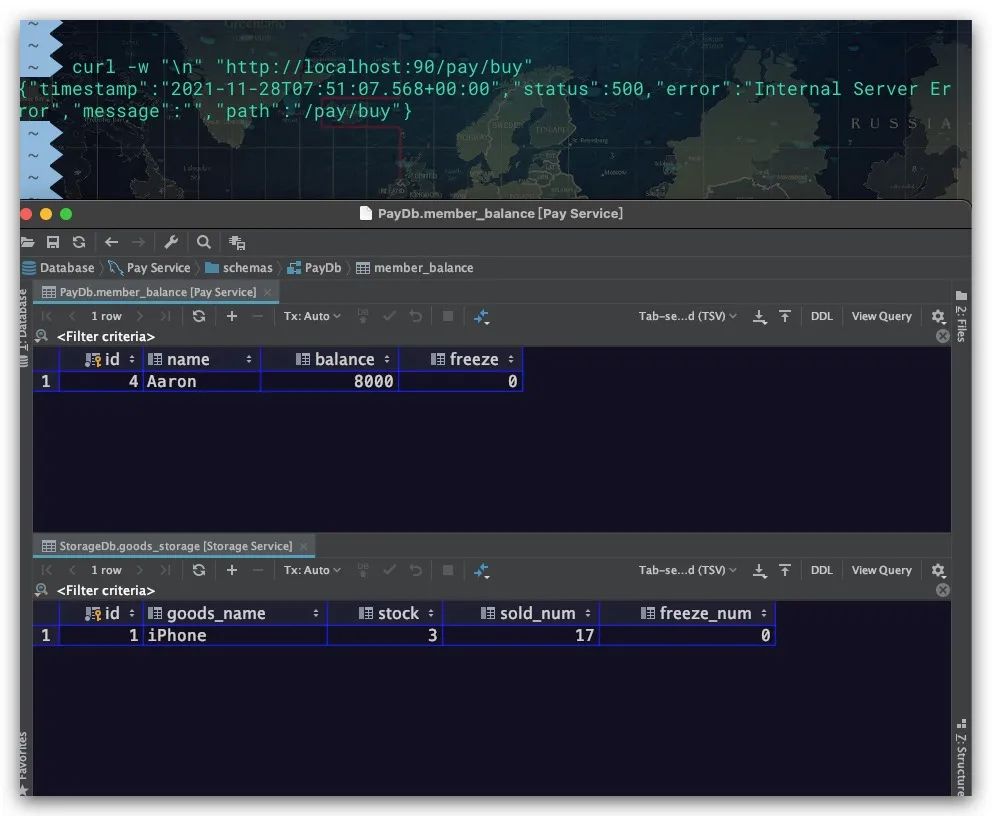
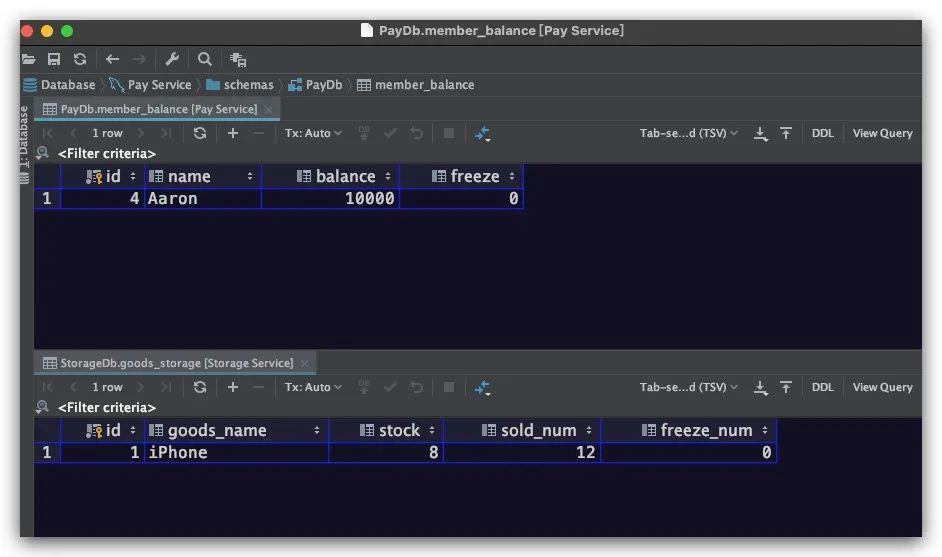
在测试之前,需要对PayService支付服务、StorageService库存服务各自的数据库完成表的建立及数据初始化工作,如下图所示
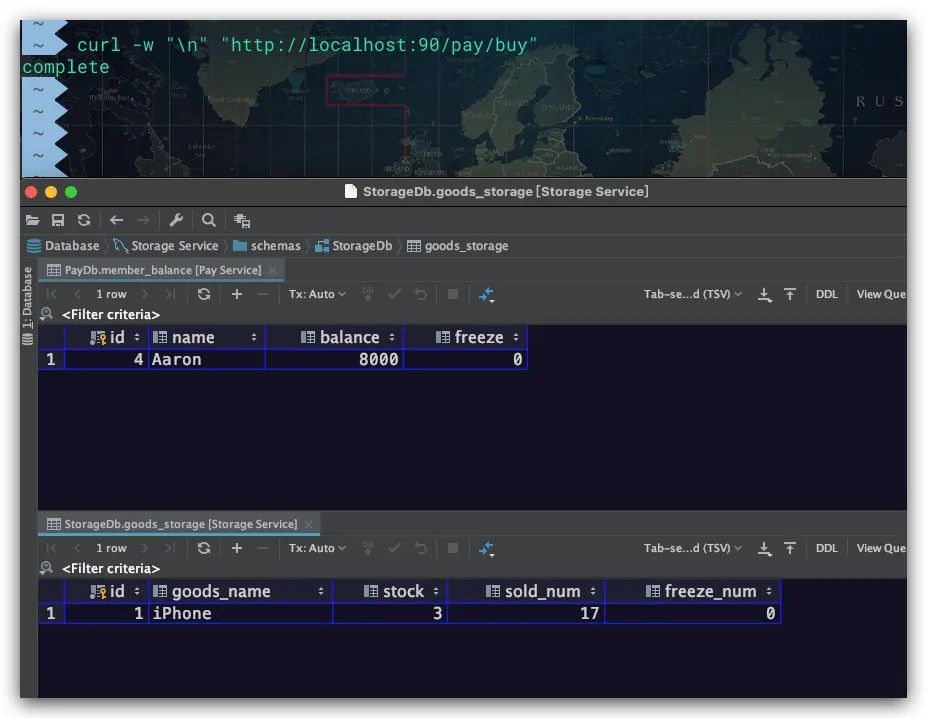
分别在90、8080端口启动PayService支付服务、StorageService库存服务,当我们第一次调用PayService支付服务的buy接口时,可以看到余额、库存均被正常扣减
而当第二次调用该接口时,由于商品库存不足。则会导致整个分布式事务进行回滚。可以看到余额、库存的数据由于被正常回滚,故未发生意外扣除