论文标题:LiDAR R-CNN: An Efficient and Universal 3D Object Detector
作者单位:TuSimple
代码:https://github.com/tusimple/LiDAR_RCNN
论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.15297.pdf
一句话读论文:
解决点云稀疏性导致的proposal尺寸歧义问题。
Different from 2D RCNN, we should equip our LiDAR-RCNN with the ability to perceive the spacing and the size of proposals.
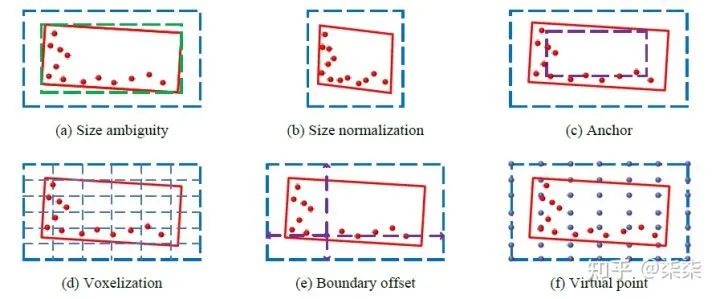
The simplest solution to the ambiguity problem is to normalize the point coordinates by the proposal size. If the proposal is enlarged, the point coordinates will be smaller and the size target will be higher. Consequently, the model could be aware of the size of the proposal.
When the R-CNN model is applied on multiple categories, it totally ignores the scale difference off different categories. The size normalization makes it more difficult for the model to distinguish different categories.
The points in it are still not aware of the voxel boundary. The model only have coarse information about the proposal size at voxel level, but not the point level. As a result, this solution alleviates, but not fully solves the ambiguity problem.
Revisiting the previous solutions, we can conclude that the key is to provide the size information to network, while preserving the shape of the object.
To provide the proposal boundary information, a simple way is to append the boundary offset to the point features. From the offset, the network will be able to know how far the points is from the proposal's boundary, which should solve the ambiguity problem.
重磅!3DCVer-学术论文写作投稿 交流群已成立
扫码添加小助手微信,可申请加入3D视觉工坊-学术论文写作与投稿 微信交流群,旨在交流顶会、顶刊、SCI、EI等写作与投稿事宜。
同时也可申请加入我们的细分方向交流群,目前主要有3D视觉、CV&深度学习、SLAM、三维重建、点云后处理、自动驾驶、多传感器融合、CV入门、三维测量、VR/AR、3D人脸识别、医疗影像、缺陷检测、行人重识别、目标跟踪、视觉产品落地、视觉竞赛、车牌识别、硬件选型、学术交流、求职交流、ORB-SLAM系列源码交流、深度估计等微信群。
一定要备注:研究方向+学校/公司+昵称,例如:”3D视觉 + 上海交大 + 静静“。请按照格式备注,可快速被通过且邀请进群。原创投稿也请联系。

▲长按加微信群或投稿 
▲长按关注公众号


▲长按关注公众号
3D视觉从入门到精通知识星球:针对3D视觉领域的视频课程(三维重建系列、三维点云系列、结构光系列、手眼标定、相机标定、orb-slam3等视频课程)、知识点汇总、入门进阶学习路线、最新paper分享、疑问解答五个方面进行深耕,更有各类大厂的算法工程人员进行技术指导。与此同时,星球将联合知名企业发布3D视觉相关算法开发岗位以及项目对接信息,打造成集技术与就业为一体的铁杆粉丝聚集区,近2000星球成员为创造更好的AI世界共同进步,知识星球入口:
学习3D视觉核心技术,扫描查看介绍,3天内无条件退款 
圈里有高质量教程资料、可答疑解惑、助你高效解决问题 觉得有用,麻烦给个赞和在看~