【关于 Distilling TS Knowledge from BERT into SNN】那些你不知道的事
作者:杨夕
论文:Distilling Task-Specific Knowledge from BERT into Simple Neural Networks
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.12136
项目地址:https://github.com/km1994/nlp_paper_study
【注:手机阅读可能图片打不开!!!】

一、动机
随着 BERT 的横空出世,意味着 上一代用于语言理解的较浅的神经网络(RNN、CNN等) 的 过时?
BERT模型是真的大,计算起来太慢了?
是否可以将BERT(一种最先进的语言表示模型)中的知识提取到一个单层BiLSTM 或 TextCNN 中?
二、论文思路
确定 Teacher 模型(Bert) 和 Student 模型(TextCNN、TextRNN);
蒸馏的两个过程:
第一,在目标函数附加logits回归部分;
第二,构建迁移数据集,从而增加了训练集,可以更有效地进行知识迁移。
三、模型框架讲解【以单句分类任务为例】
3.1 Teacher 模型(Bert) 微调
Bert 模型 模型构建
构建 Bert 模型,然后将 Bert 输出的句子的向量表示过dense层和softmax层,得到logits输出,代码如下:
代码实现:
class BertClassification(BertPreTrainedModel): def __init__(self, config, num_labels=2): super(BertClassification, self).__init__(config) self.num_labels = num_labels self.bert = BertModel(config) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob) self.classifier = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, num_labels) self.init_weights()
def forward(self, input_ids, input_mask, label_ids): _, pooled_output = self.bert(input_ids, None, input_mask) pooled_output = self.dropout(pooled_output) logits = self.classifier(pooled_output) if label_ids is not None: loss_fct = CrossEntropyLoss() return loss_fct(logits.view(-1, self.num_labels), label_ids.view(-1)) return logits
Bert 模型微调
代码实现:
def main(model_type="bert",bert_model='bert-base-chinese', cache_dir=None, max_seq=128, batch_size=16, num_epochs=10, lr=2e-5): processor = Processor() train_examples = processor.get_train_examples('data/hotel') label_list = processor.get_labels() tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(bert_model, do_lower_case=True) if model_type=="bert": model = BertClassification.from_pretrained(bert_model, cache_dir=cache_dir, num_labels=len(label_list)) else: model = BertTextCNN.from_pretrained(bert_model,cache_dir=cache_dir,num_labels=len(label_list)) model.to(device) param_optimizer = list(model.named_parameters()) no_decay = ['bias', 'LayerNorm.bias', 'LayerNorm.weight'] optimizer_grouped_parameters = [ {'params': [p for n, p in param_optimizer if not \ any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)], 'weight_decay': 0.01}, {'params': [p for n, p in param_optimizer if \ any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)], 'weight_decay': 0.00}] print('train...') num_train_steps = int(len(train_examples) / batch_size * num_epochs) optimizer = AdamW(optimizer_grouped_parameters, lr=lr) train_features = convert_examples_to_features(train_examples, label_list, max_seq, tokenizer) all_input_ids = torch.tensor([f.input_ids for f in train_features], dtype=torch.long) all_input_mask = torch.tensor([f.input_mask for f in train_features], dtype=torch.long) all_label_ids = torch.tensor([f.label_id for f in train_features], dtype=torch.long) train_data = TensorDataset(all_input_ids, all_input_mask, all_label_ids) train_sampler = RandomSampler(train_data) train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_data, sampler=train_sampler, batch_size=batch_size) model.train() for _ in trange(num_epochs, desc='Epoch'): tr_loss = 0 for step, batch in enumerate(tqdm(train_dataloader, desc='Iteration')): input_ids, input_mask, label_ids = tuple(t.to(device) for t in batch) loss = model(input_ids, input_mask, label_ids) loss.backward() optimizer.step() optimizer.zero_grad() tr_loss += loss.item() print('tr_loss', tr_loss) print('eval...') eval_examples = processor.get_dev_examples('data/hotel') eval_features = convert_examples_to_features(eval_examples, label_list, max_seq, tokenizer) eval_input_ids = torch.tensor([f.input_ids for f in eval_features], dtype=torch.long) eval_input_mask = torch.tensor([f.input_mask for f in eval_features], dtype=torch.long) eval_label_ids = torch.tensor([f.label_id for f in eval_features], dtype=torch.long) eval_data = TensorDataset(eval_input_ids, eval_input_mask, eval_label_ids) eval_sampler = SequentialSampler(eval_data) eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_data, sampler=eval_sampler, batch_size=batch_size) model.eval() preds = [] for batch in tqdm(eval_dataloader, desc='Evaluating'): input_ids, input_mask, label_ids = tuple(t.to(device) for t in batch) with torch.no_grad(): logits = model(input_ids, input_mask, None) preds.append(logits.detach().cpu().numpy()) preds = np.argmax(np.vstack(preds), axis=1) print(compute_metrics(preds, eval_label_ids.numpy())) torch.save(model, f'data/cache/{model_type}_model')
3.2 Student 模型(TextCNN、TextRNN)构建
3.2.1 TextRNN 模型构建
模型结构:sentence -> Embedding Layer -> Word Embeddings -> BiLSTM -> Hidden States (Bidirection) -> dense -> Relu -> dense -> logits ->softmax
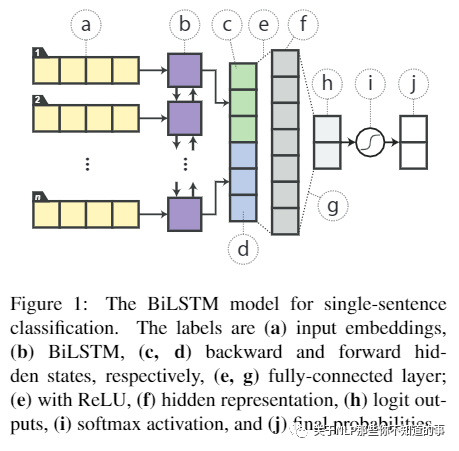
单句子分类的BiLSTM模型。标签分别是(a)输入 emb,(b)BiLSTM,(c,d)向后和向前 hidden 状态,(e,g)全连接层,(e)带ReLU,(f)隐藏表示,(h)logit outputs,(i)softmax 激活函数,和(j)最终概率
代码实现:
class RNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, x_dim, e_dim, h_dim, o_dim): super(RNN, self).__init__() self.h_dim = h_dim self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2) self.emb = nn.Embedding(x_dim, e_dim, padding_idx=0) self.lstm = nn.LSTM(e_dim, h_dim, bidirectional=True, batch_first=True) self.fc = nn.Linear(h_dim * 2, o_dim) self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1) self.log_softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x, lens): embed = self.dropout(self.emb(x)) out, _ = self.lstm(embed) hidden = self.fc(out[:, -1, :]) return self.softmax(hidden), self.log_softmax(hidden)
3.2.2 TextCNN 模型构建
模型结构:sentence -> Embedding Layer -> Word Embeddings -> dropout -> Conv -> Relu -> max_pool1d -> cat -> dropout -> dense -> logits ->softmax
代码实现:
class CNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, x_dim, e_dim, h_dim, o_dim): super(CNN, self).__init__() self.emb = nn.Embedding(x_dim, e_dim, padding_idx=0) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2) self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, h_dim, (3, e_dim)) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(1, h_dim, (4, e_dim)) self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(1, h_dim, (5, e_dim)) self.fc = nn.Linear(h_dim * 3, o_dim) self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1) self.log_softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x, lens): embed = self.dropout(self.emb(x)).unsqueeze(1) c1 = torch.relu(self.conv1(embed).squeeze(3)) p1 = torch.max_pool1d(c1, c1.size()[2]).squeeze(2) c2 = torch.relu(self.conv2(embed).squeeze(3)) p2 = torch.max_pool1d(c2, c2.size()[2]).squeeze(2) c3 = torch.relu(self.conv3(embed).squeeze(3)) p3 = torch.max_pool1d(c3, c3.size()[2]).squeeze(2) pool = self.dropout(torch.cat((p1, p2, p3), 1)) hidden = self.fc(pool) return self.softmax(hidden), self.log_softmax(hidden)
3.3 Distillation Objective
在 3.1、3.2 节,我们分别介绍了 Teacher 模型(Bert)和 Student 模型(TextCNN、TextRNN),那么现在问题来了:“如何 才能将 Teacher 模型 的知识迁移到Student 模型中呢?”
在 论文中,作者主要将 Teacher 模型的 logits 输出作为 Student 模型的 Distillation Objective,通过这种方式 将 Teacher 模型 的知识迁移到 Student 模型中,公式如下所示:
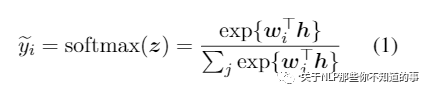
Teacher 模型的 logits 输出
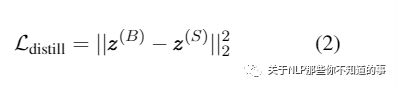
Student 网络的 logits 与 Teacher logits 之间的均方误差(MSE)损失
其中:ZB 为 Teacher logits,ZS 为 Student logits
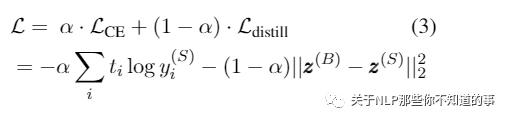
Loss函数
注:t 为真实标签,如果迁移集不带标签,那么t是通过大模型softmax输出转换得到的ont-hot向量; 是小模型的softmax输出
代码实现:
Teacher 模型的 logits 输出
class Teacher(object): def __init__(self, bert_model='bert-base-chinese', max_seq=128): self.max_seq = max_seq self.tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained( bert_model, do_lower_case=True) self.model = torch.load('./data/cache/model') self.model.eval()
def predict(self, text): tokens = self.tokenizer.tokenize(text)[:self.max_seq] input_ids = self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens) input_mask = [1] * len(input_ids) padding = [0] * (self.max_seq - len(input_ids)) input_ids = torch.tensor([input_ids + padding], dtype=torch.long).to(device) input_mask = torch.tensor([input_mask + padding], dtype=torch.long).to(device) logits = self.model(input_ids, input_mask, None) return F.softmax(logits, dim=1).detach().cpu().numpy()
Distillation目标函数
model = RNN(v_size, 256, 256, 2) # model = CNN(v_size,256,128,2) if USE_CUDA: model = model.cuda() opt = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr) ce_loss = nn.NLLLoss() mse_loss = nn.MSELoss() for epoch in range(epochs): losses = [] accu = [] model.train() for i in range(0, len(x_tr), b_size): model.zero_grad() bx = Variable(LTensor(x_tr[i:i + b_size])) by = Variable(LTensor(y_tr[i:i + b_size])) bl = Variable(LTensor(l_tr[i:i + b_size])) bt = Variable(FTensor(t_tr[i:i + b_size])) py2 = model(bx, bl) loss = alpha * ce_loss(py2, by) + (1-alpha) * mse_loss(py1, bt) # in paper, only mse is used loss.backward() opt.step() losses.append(loss.item()) for i in range(0, len(x_de), b_size): model.zero_grad() bx = Variable(LTensor(x_de[i:i + b_size])) bl = Variable(LTensor(l_de[i:i + b_size])) bt = Variable(FTensor(t_de[i:i + b_size])) py2 = model(bx, bl) loss = mse_loss(py1, bt) if teach_on_dev: # train only with teacher on dev set losses.append(loss.item())
四、Data Augmentation for Distillation
动机:在上文中,我们介绍了 如何 将 Teacher 模型 的知识迁移到Student 模型中,但是对于小数据集而言,在 Distillation 过程中,容易出现无法完全表达大模型的知识问题,导致模型出现过拟合,那有没有比较好的解决方法呢?
方法:数据增强。即 利用数据增强的方法认为扩充数据集,来防止过拟合
思路:
Masking:以一定的概率,用[MASK]标签来取代句子中的某个单词;
POS-guided word replacement:以一定的概率,用同词性的词来取代当前词。根据原始训练集中同词性词语的词频来确定取代词;
n-gram sampling:以一定的概率,用n-gram来取代原始的句子。n的取值范围是[1,5]。这个操作相当于dropout,是升级版的Masking。
步骤:
先遍历句子中的每个单词,对每个单词产生一个平均分布的[0,1]区间的概率。根据概率落在的区间,选择用Masking还是POS方式替换当前词;
遍历完成后,以一定的概率选择是否进行n-gram sampling;
对每个句子,进行n_{iter}增强,产生n_{iter}个伪数据。对句对匹配任务,固定第一个句子、第二个句子、两个句子都不固定,进行3 n_{iter}数据增强。
五、单句分类任务 实验结果分析
5.1 数据集介绍
本文所用的数据集 为 一个 关于酒店的二分类数据,该数据样式如下:
1 闹中取静的一个地方,在窗前能看到不错的风景。酒店价格的确有些偏高0 房价要四百多,但感到非常失望,陈旧,脏,比锦江之星还差。以后肯定不会再去了。这样的硬件设施和服务怎么吸引客人呢。1 酒店总体感觉不错,很适合外宾入住,大堂的氛围整个就像是一个外国人的社区。房间很舒服,携程搞活动,还加送了红酒和水果,很不错,下次还会考虑入住。只是停车场比较麻烦,来宾进停车场之前还要有狼狗绕车检查,感觉不舒服。0 好小的门面,没有电梯,房间也不是很一致!豪华房居然要400多,马桶还是坏的!酒店太自作主张了。。。。0 房间以次充好,提出异议后才调整,调整后还是较差的房间0 面前就是高架,实在是太吵了,一晚上没睡! ...
5.2 实验结果分析
| 模型 | Acc | F1 | 速度 |
| Bert | 0.9 | 0.9051458382736542 | 0.24132323265075684 s |
| TextCNN | 0.8263671882450581 | 0.8271728271728271 | 0.001s |
| Bert->TextCNN | 0.88125 | 0.8883666274970623 | 0.004960536956787109 s |
六、总结
Bert->TextCNN 模型 虽然 效果 低于 Bert,但是 比 直接用 TextCNN 高很多;
Bert->TextCNN 模型 虽然 推理速度 低于 TextCNN,但是 比 直接用 Bert 高很多;
参考资料
基于BERT的蒸馏实验
知识蒸馏论文选读(二)
知识蒸馏(Knowledge Distillation
