机器学习算法-随机森林之决策树R 代码从头暴力实现(3)
共 443字,需浏览 1分钟
· 2021-01-13
前文 (机器学习算法 - 随机森林之决策树初探(1)) 讲述了决策树的基本概念、决策评价标准并手算了单个变量、单个分组的Gini impurity。是一个基本概念学习的过程,如果不了解,建议先读一下再继续。
机器学习算法-随机森林之决策树R 代码从头暴力实现(2)通过 R 代码从头暴力方式自写函数训练决策树,已决策出第一个节点。后续......
再决策第二个节点、第三个节点
第一个决策节点找好了,后续再找其它决策节点。如果某个分支的点从属于多个class,则递归决策。
递归决策终止的条件是:
再添加分支不会降低
Gini impurity某个分支的数据点属于同一分类组 (
Gini impurity = 0)
定义函数如下:
brute_descition_tree_result <- list()
brute_descition_tree_result_index <- 0
# 递归分支决策
brute_descition_tree <- function(data, measure_variable, class_variable, type="Root"){
# 计算初始Gini值
Init_gini_impurity <- Gini_impurity(data[[class_variable]])
# 确定当前需要决策的节点的最优变量和最优阈值
brute_force_result <- Gini_impurity_for_all_possible_branches_of_all_variables(
data, variables, class=class_variable, Init_gini_impurity=Init_gini_impurity)
# 输出中间计算结果
print(brute_force_result)
# 根据最优决策变量、阈值和Gini增益
split_variable <- brute_force_result[1,1]
split_threshold <- brute_force_result[1,2]
gini_gain = brute_force_result[1,5]
# print(gini_gain)
# 判断此次决策是否需要保留
if(gini_gain>0){
brute_descition_tree_result_index <<- brute_descition_tree_result_index + 1
brute_descition_tree_result[[brute_descition_tree_result_index]] <<-
c(type=type, split_variable=split_variable,
split_threshold=split_threshold)
# print(brute_descition_tree_result_index)
# print(brute_descition_tree_result)
# 决策左右分支
left <- data[data[split_variable] right <- data[data[split_variable]>=split_threshold,]
# 分别对左右分支进一步决策
if(length(unique(left[[class_variable]]))>1){
brute_descition_tree(data=left, measure_variable, class_variable,
type=paste(brute_descition_tree_result_index, "left"))
}
if(length(unique(right[[class_variable]]))>1){
brute_descition_tree(data=right, measure_variable, class_variable,
type=paste(brute_descition_tree_result_index, "right"))
}
}
# return(brute_descition_tree_result)
}
调用函数,并输出中间计算结果
brute_descition_tree(data, variables, "color")
根节点评估记录
## Variable Threshold Left_branch Right_branch Gini_gain
## 5 x 1.95 blue x 3; red x 2 green x 5 0.38
## 3 x 1.45 blue x 3 green x 5; red x 2 0.334285714285714
## 31 y 1.75 blue x 3 green x 5; red x 2 0.334285714285714
## 4 x 1.85 blue x 3; red x 1 green x 5; red x 1 0.303333333333333
## 6 x 2.25 blue x 3; green x 1; red x 2 green x 4 0.253333333333333
## 41 y 2.05 blue x 3; green x 1 green x 4; red x 2 0.203333333333333
## 2 x 0.8 blue x 2 blue x 1; green x 5; red x 2 0.195
## 21 y 1.25 blue x 2 blue x 1; green x 5; red x 2 0.195
## 51 y 2.15 blue x 3; green x 1; red x 1 green x 4; red x 1 0.18
## 7 x 2.75 blue x 3; green x 2; red x 2 green x 3 0.162857142857143
## 71 y 2.9 blue x 3; green x 2; red x 2 green x 3 0.162857142857143
## 61 y 2.5 blue x 3; green x 2; red x 1 green x 3; red x 1 0.103333333333333
## 8 x 3.3 blue x 3; green x 3; red x 2 green x 2 0.095
## 81 y 3.15 blue x 3; green x 3; red x 2 green x 2 0.095
## 1 x 0.25 blue x 1 blue x 2; green x 5; red x 2 0.0866666666666667
## 11 y 0.75 blue x 1 blue x 2; green x 5; red x 2 0.0866666666666667
## 9 x 3.65 blue x 3; green x 4; red x 2 green x 1 0.0422222222222223
## 91 y 3.4 blue x 3; green x 4; red x 2 green x 1 0.0422222222222223
第二层节点评估记录
## Variable Threshold Left_branch Right_branch Gini_gain
## 3 x 1.45 blue x 3 red x 2 0.48
## 31 y 1.8 blue x 3 red x 2 0.48
## 2 x 0.8 blue x 2 blue x 1; red x 2 0.213333333333333
## 21 y 1.25 blue x 2 blue x 1; red x 2 0.213333333333333
## 4 x 1.85 blue x 3; red x 1 red x 1 0.18
## 41 y 2.45 blue x 3; red x 1 red x 1 0.18
## 1 x 0.25 blue x 1 blue x 2; red x 2 0.08
## 11 y 0.75 blue x 1 blue x 2; red x 2 0.08
最终选择的决策变量和决策阈值
as.data.frame(do.call(rbind, brute_descition_tree_result))
最终选择的决策变量和决策阈值
## type split_variable split_threshold
## 1 Root x 1.95
## 2 2 left x 1.45
运行后,获得两个决策节点,绘制决策树如下:
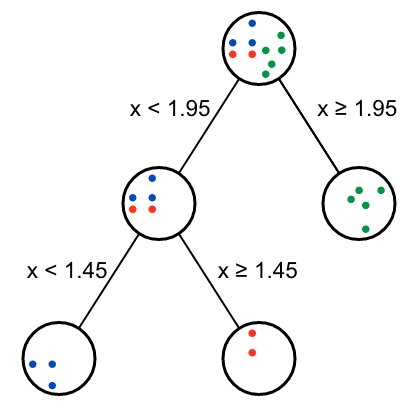
从返回的Gini gain表格可以看出,第二个节点有两种效果一样的分支方式。
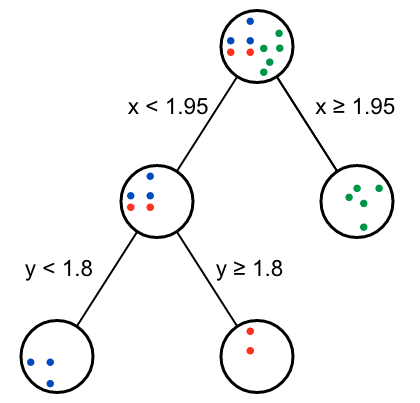
这样我们就用暴力方式完成了决策树的构建。
https://victorzhou.com/blog/intro-to-random-forests/
https://victorzhou.com/blog/gini-impurity/
https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/192310/is-random-forest-suitable-for-very-small-data-sets
https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-random-forest-58381e0602d2
https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/RandomForests/reg_philosophy.html
https://medium.com/@williamkoehrsen/random-forest-simple-explanation-377895a60d2d
往期精品(点击图片直达文字对应教程)
后台回复“生信宝典福利第一波”或点击阅读原文获取教程合集
(请备注姓名-学校/企业-职务等)




























